Introduction
As people become more health-conscious, the demand for natural sweeteners like honey, agave, and stevia is rising. Many are looking for ways to reduce sugar intake while still enjoying sweetness. But are these natural alternatives really healthier than traditional sugar?
In this article, we will explore the differences between natural sweeteners and sugar, examining their health benefits and potential risks. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of whether natural sweeteners truly live up to the hype.
Understanding Sugar and Its Health Impacts
The Basics of Sugar
Sugar is a type of carbohydrate that occurs naturally in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. The most common form of sugar found in our diets is sucrose, derived from sugarcane or sugar beets. Other sugars, such as fructose and glucose, are naturally present in various foods, and our bodies use them as a primary source of energy.
However, the real health concern arises when we consume added sugars. These are sugars that are introduced into foods during processing or preparation, as opposed to those naturally occurring in whole foods. Examples include table sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, and other sweeteners added to processed foods. These added sugars contribute to empty calories and often lack essential nutrients.
Health Concerns Linked to Excessive Sugar Consumption
Overconsumption of sugar, particularly added sugars, is linked to a wide range of health issues. Studies have shown that a high intake of sugar can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Excessive sugar consumption is also associated with heart disease, fatty liver disease, and high blood pressure.
When we consume large amounts of sugar, our bodies experience spikes in blood glucose levels. These spikes can cause inflammation and, over time, lead to the development of chronic diseases. The risk of obesity is especially concerning because it sets the stage for other conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
The Role of Sugar in the Diet
While sugar itself isn't inherently bad, moderation is key. It's important to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars, such as those in fruits and vegetables, and added sugars. Naturally occurring sugars come with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that are beneficial for health. On the other hand, added sugars provide little nutritional value and contribute to unhealthy calorie consumption.
Health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), recommend limiting added sugar intake to less than 10% of total daily calories. For most adults, this equates to no more than 50 grams of added sugar per day, which is roughly equivalent to about 12 teaspoons.
Aspect | Natural Sweeteners | Refined Sugar |
Source | Plant-based (e.g., honey, stevia, agave) | Processed from sugarcane or sugar beets |
Nutritional Value | Contains some vitamins, minerals, antioxidants | Provides empty calories, no nutrients |
Glycemic Index | Low (e.g., stevia, monk fruit) | High, causes rapid blood sugar spikes |
Calories | Low or moderate (e.g., stevia, agave) | High in calories, contributes to weight gain |
Health Benefits | Potential antioxidants, gut health benefits | No health benefits, linked to diseases |
Exploring Natural Sweeteners
What Are Natural Sweeteners?
Natural sweeteners are derived from plant-based sources and typically undergo minimal processing compared to refined sugars. Some popular examples of natural sweeteners include:
● Honey: Produced by bees from nectar, honey contains small amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
● Agave nectar: Extracted from the agave plant, this sweetener is known for its mild taste and low glycemic index.
● Maple syrup: Harvested from maple trees, maple syrup contains some beneficial nutrients like manganese and zinc.
● Stevia: A plant-based sweetener that is hundreds of times sweeter than sugar, often used in small quantities to sweeten foods and drinks.
Natural sweeteners are often marketed as healthier alternatives to refined sugars due to their minimal processing and the presence of some beneficial nutrients. However, it's important to evaluate them based on their actual health benefits and potential risks.
Key Differences Between Natural and Refined Sugar
The primary difference between natural sweeteners and refined sugar lies in their processing. Refined sugar is extracted and processed in such a way that it loses most of its nutrients, leaving behind "empty calories." In contrast, natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup retain small amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which provide additional nutritional value.
Another difference is that natural sweeteners tend to have a lower glycemic index (GI) than refined sugar. The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Sweeteners like stevia and agave nectar have a lower GI, meaning they cause slower, more gradual increases in blood sugar compared to traditional sugar.
Nutritional Profile of Natural Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners often contain small amounts of nutrients that are absent in refined sugars. For instance, honey contains antioxidants, while maple syrup provides manganese and zinc. However, the amounts of these nutrients are relatively small, and you would need to consume large quantities to achieve any significant health benefits. Still, compared to refined sugar, these sweeteners can offer some added value beyond just sweetness.
It's important to note that while natural sweeteners may offer a slightly better nutritional profile than refined sugar, they are not "superfoods" and should still be consumed in moderation.
Health Benefits of Natural Sweeteners
Lower Glycemic Index and Blood Sugar Regulation
One of the key selling points of natural sweeteners is their lower glycemic index. Sweeteners like stevia, monk fruit, and agave nectar are less likely to cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, making them a better choice for individuals with diabetes or those managing blood sugar levels. The low GI of these sweeteners means that they are absorbed more slowly by the body, leading to a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream.
While they do not have zero impact on blood sugar levels, their lower glycemic index makes them a healthier option compared to refined sugar, which can lead to sharp increases in blood glucose and insulin levels.
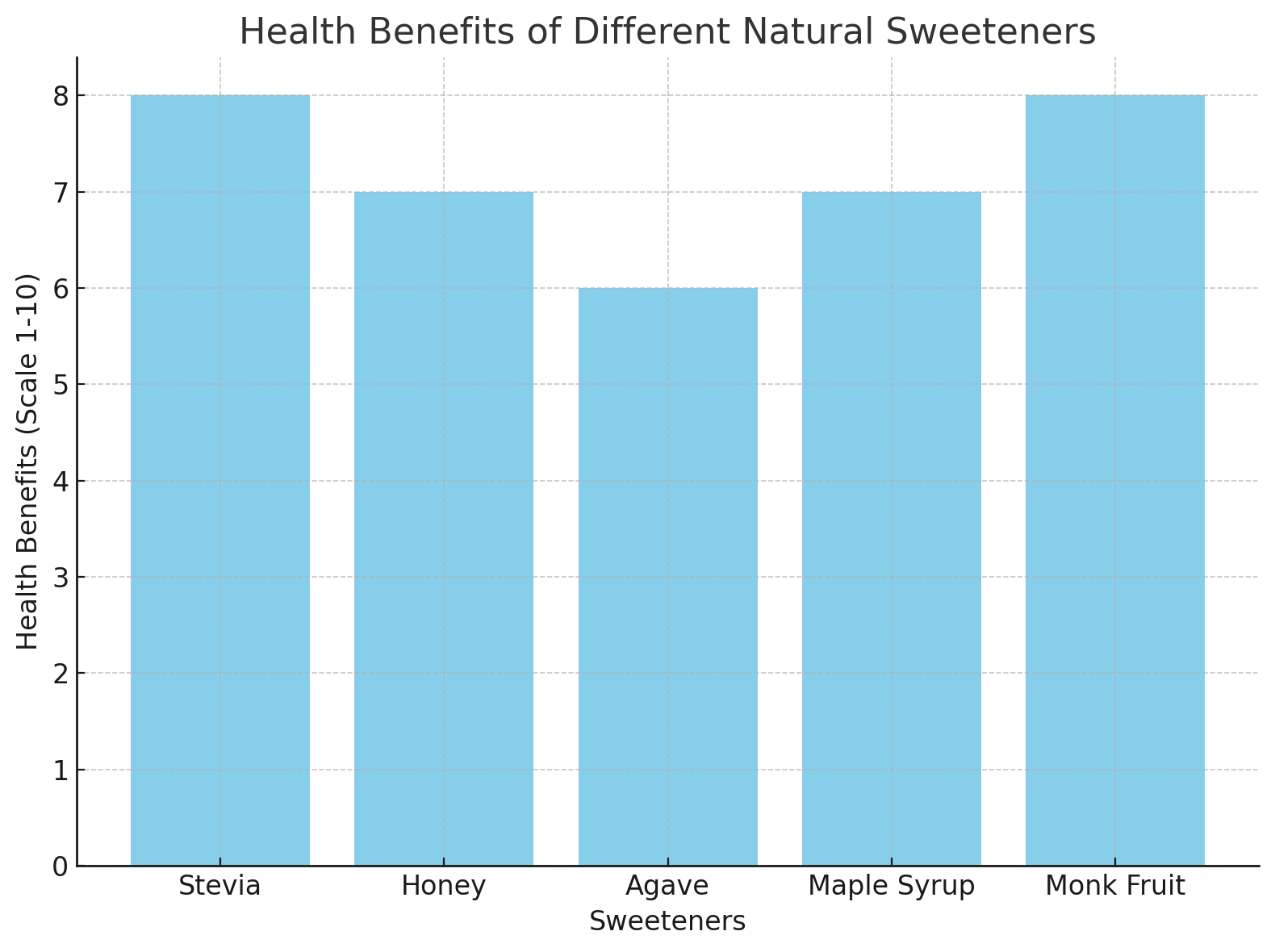
Natural Sweetener | Health Benefits |
Stevia | Low glycemic index, suitable for diabetes, zero calories |
Honey | Contains antioxidants, antibacterial properties |
Agave Nectar | Low glycemic index, gut health support (prebiotics) |
Maple Syrup | Rich in antioxidants, manganese, and zinc |
Monk Fruit | Antioxidants, zero calories, low glycemic index |
Nutritional Value Beyond Sweetness
In addition to offering a sweeter taste, many natural sweeteners provide small amounts of essential nutrients. For example, honey contains antioxidants that help fight oxidative stress, and maple syrup offers trace minerals like manganese and zinc that support immune function. These nutrients, though present in small quantities, can contribute to overall health, especially when used in place of processed sugars that offer no nutritional value.
Natural sweeteners also contain fewer artificial additives and preservatives compared to their synthetic counterparts, making them a more natural choice for consumers looking to avoid chemicals in their diets.
Gut Health and Prebiotics
Certain natural sweeteners, particularly agave nectar, contain prebiotics, which promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. These prebiotics help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for digestion, immunity, and overall health. While the prebiotic effects of agave nectar are modest, they are an added benefit compared to refined sugar, which offers no such advantages for gut health.
Potential Risks of Natural Sweeteners
High Caloric Content in Some Natural Sweeteners
Although natural sweeteners are often considered healthier alternatives to refined sugar, they are not calorie-free. Some, like honey and maple syrup, contain a significant amount of calories and carbohydrates, which can contribute to weight gain if consumed excessively. For individuals looking to reduce their caloric intake, these sweeteners should still be used in moderation.
While natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit are lower in calories, other options like agave nectar are high in fructose, which can lead to metabolic issues when consumed in large quantities.
Possible Impact on Metabolic Health
Despite the benefits of natural sweeteners, they can still have an impact on metabolic health if consumed in excess. For example, while agave nectar has a lower glycemic index, it is high in fructose, which can contribute to insulin resistance, fatty liver disease, and increased triglyceride levels. Additionally, honey, while providing some antioxidants, is calorie-dense and can contribute to weight gain if not consumed in moderation.
Allergic Reactions and Other Side Effects
Some natural sweeteners, such as honey and agave, may cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Honey can trigger reactions in people allergic to bee stings, while agave nectar may cause digestive discomfort for some due to its high fructose content. It's essential to be mindful of potential side effects and choose natural sweeteners that work well with your body.
Risk | Natural Sweetener | Potential Impact |
Caloric Intake | Honey, Maple Syrup, Agave | May contribute to weight gain if consumed excessively |
Digestive Issues | Agave, High fructose sweeteners | May cause bloating, gas, or discomfort due to high fructose content |
Metabolic Health | Agave, Honey | Excessive consumption may lead to insulin resistance, fatty liver |
Allergic Reactions | Honey | Can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals |
Comparing Natural Sweeteners with Artificial Sweeteners
The Rise of Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, are commonly used as sugar substitutes in "diet" products and sugar-free foods. These sweeteners are chemically synthesized and offer little to no calories, making them attractive for weight management and diabetes control. However, the long-term health effects of artificial sweeteners remain a subject of debate.
Safety Concerns Around Artificial Sweeteners
While artificial sweeteners are generally recognized as safe by regulatory bodies like the FDA, there are concerns about their long-term health effects. Some studies have suggested potential links between artificial sweeteners and cancer, metabolic disorders, and changes in gut bacteria. However, most of these studies are inconclusive, and more research is needed to determine the true risks of artificial sweeteners.
Pros and Cons of Choosing Natural Over Artificial Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners offer a more whole-food-based alternative to artificial sweeteners, which are often highly processed. While both types of sweeteners can help reduce sugar intake, natural sweeteners come with the added benefit of containing small amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. However, they still contain calories and can impact metabolic health if consumed excessively. On the other hand, artificial sweeteners are calorie-free but may have unknown long-term health consequences.

Expert Opinions on Natural Sweeteners and Health
The Perspective of Nutritionists and Dietitians
Nutrition experts generally recommend moderation when it comes to sweeteners, whether natural or artificial. While natural sweeteners may offer some health benefits, such as lower glycemic index and additional nutrients, they are still sugars and should be used sparingly. For those looking to improve their health, focusing on a whole-food-based diet with limited added sugars is the best approach.
The World Health Organization’s Stance on Sweeteners
The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued guidelines suggesting that non-sugar sweeteners, both artificial and natural, should not be used as a strategy for weight management or disease prevention. According to the WHO, reducing overall sugar intake by focusing on whole, unprocessed foods is the most effective way to improve health and prevent chronic diseases.
Conclusion
Natural sweeteners offer a healthier alternative to refined sugar, providing some nutritional benefits like antioxidants and a lower glycemic index. However, they still carry risks if consumed in excess, potentially leading to weight gain and metabolic issues. For better health, it’s important to maintain a balanced diet, focusing on whole foods and limiting added sugars. Companies like Zhuhai Huichun Trade Co.,Ltd. offer a range of natural sweeteners that can help reduce sugar intake while supporting a healthier lifestyle.
FAQ
Q: What are natural sweeteners?
A: Natural sweeteners are plant-based alternatives to refined sugar, including options like honey, stevia, and agave nectar. They are often seen as healthier due to their minimal processing and potential nutritional benefits.
Q: Are natural sweeteners better for your health than sugar?
A: While natural sweeteners can be a healthier alternative to refined sugar, they still contain calories and should be consumed in moderation. Overconsumption can lead to weight gain and metabolic issues, just like regular sugar.
Q: How do natural sweeteners affect blood sugar levels?
A: Many natural sweeteners, such as stevia and monk fruit, have a low glycemic index and cause less fluctuation in blood sugar levels compared to refined sugar. This makes them a suitable option for managing blood sugar levels.
Q: Are natural sweeteners safe for people with diabetes?
A: Some natural sweeteners, like stevia, are safe for people with diabetes due to their low glycemic index. However, it's important to monitor the quantity consumed to avoid excessive calorie intake.
Q: Do natural sweeteners have any nutritional benefits?
A: Yes, some natural sweeteners, such as honey and maple syrup, contain small amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, providing more nutritional value than refined sugar.
Q: Can natural sweeteners help with weight loss?
A: Natural sweeteners, when used in moderation, may help reduce calorie intake compared to sugar, potentially supporting weight loss. However, excessive consumption can still contribute to weight gain.
Q: How do natural sweeteners compare to artificial sweeteners?
A: Natural sweeteners are generally considered safer than artificial sweeteners, which are chemically processed. Natural sweeteners often offer some nutritional value and fewer long-term health risks.
Q: Are there any risks associated with using natural sweeteners?
A: While natural sweeteners are often healthier than refined sugar, they can still contribute to weight gain or digestive issues if consumed in excess. Moderation is key for maintaining overall health.















