Introduction
Natural sweeteners have gained popularity as healthier alternatives to refined sugar. As people become more health-conscious, these sweeteners provide a natural way to enjoy sweetness without the negative effects of sugar. In this article, we will explore the different types of natural sweeteners, their benefits, and how they compare to traditional sugar.
What Are Natural Sweeteners?
Definition and Basic Function
Natural sweeteners are substances derived from plants or animals, often with minimal processing. Unlike refined sugars, which are extracted from sugarcane or sugar beets through heavy processing, natural sweeteners are typically closer to their original form. Examples of natural sweeteners include honey, maple syrup, stevia, and agave syrup. These sweeteners provide sweetness without the high glycemic impact of regular sugar and are often favored for their additional nutrients and health benefits.
Benefits of Natural Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners offer several key benefits over conventional sugar. They typically have a lower glycemic index, meaning they cause slower and more stable increases in blood sugar levels. This makes them a better option for people managing diabetes or those trying to reduce their overall sugar intake. Additionally, many natural sweeteners contain antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that refined sugar lacks. For instance, honey and maple syrup contain valuable compounds like antioxidants that can support immune health and provide anti-inflammatory effects.
Common Natural Sweeteners
There are many types of natural sweeteners, each with its unique flavor profile and health benefits. Some of the most common include:
● Honey: Known for its versatility and floral taste, honey is rich in antioxidants and can be used in a variety of dishes, from teas to baked goods.
● Stevia: A calorie-free, plant-based sweetener that is much sweeter than sugar, stevia has become a popular choice for people looking to reduce their calorie intake.
● Maple Syrup: This syrup is made from the sap of maple trees and has a rich, earthy flavor. It contains minerals like zinc and manganese, making it a healthier option than traditional refined sugar.
● Agave Syrup: Extracted from the agave plant, this syrup has a mild sweetness and is often used as a vegan alternative to honey.
● Monk Fruit: Known for its high sweetness with zero calories, monk fruit is becoming popular as a sugar substitute, especially for people who want to control their blood sugar levels.

How Do Natural Sweeteners Work in the Body?
Metabolism and Absorption
Natural sweeteners are metabolized differently than regular sugar. While refined sugar is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, causing rapid spikes in blood sugar, many natural sweeteners are absorbed more slowly. This is due to their lower glycemic index, which helps prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes. Some sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit have little to no effect on blood glucose levels, making them suitable for diabetics and those seeking to maintain stable energy levels.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup do impact blood sugar levels but at a slower pace compared to refined sugar. On the other hand, sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit do not cause blood sugar increases. This makes them ideal for individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels or those following low-carb or ketogenic diets. Understanding how each natural sweetener affects blood sugar is important when choosing the right one for your health needs.
Nutritional Benefits
Unlike refined sugar, natural sweeteners often contain trace amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. For example, honey contains small amounts of vitamins B6 and C, as well as trace minerals like calcium and iron. Maple syrup also provides manganese, zinc, and calcium. These nutrients can help support overall health and make natural sweeteners a more nutritious choice than conventional sugar.
Types of Natural Sweeteners
Honey
Honey is one of the most popular natural sweeteners, used in everything from teas to baked goods. It contains antioxidants, enzymes, and a small amount of vitamins and minerals. Honey has been shown to have antibacterial properties and can aid in digestion. However, it is still a sugar and should be used in moderation to avoid excessive calorie intake. Its versatility and natural composition make it a favored option for those seeking a healthier alternative to refined sugar.
Stevia
Stevia is a plant-derived sweetener that is incredibly sweet, yet contains no calories. It is often used as a sugar substitute in beverages, desserts, and cooking. Stevia is also safe for individuals with diabetes as it does not raise blood sugar levels. Its sweetness is many times stronger than sugar, so only a small amount is needed to achieve the desired sweetness. This makes it a great option for people looking to cut calories without sacrificing sweetness.
Maple Syrup
Maple syrup, made from the sap of maple trees, offers a rich flavor and several health benefits. It contains important minerals like manganese, zinc, and calcium, which support bone health and immune function. Unlike refined sugar, maple syrup has a lower glycemic index, meaning it causes slower increases in blood sugar. Despite its health benefits, it is still a sugar and should be used in moderation.
Coconut Sugar
Coconut sugar is made from the sap of the coconut tree and has a lower glycemic index than regular sugar. It also contains trace minerals such as iron, calcium, and potassium. Coconut sugar is often used as a one-to-one replacement for regular sugar in baking and cooking. Its flavor is similar to brown sugar, making it a great choice for people who enjoy rich, caramel-like sweetness.
Monk Fruit
Monk fruit is a small, round fruit native to Southeast Asia. It is known for being incredibly sweet, yet contains zero calories. Monk fruit sweeteners do not raise blood sugar levels, making them ideal for diabetics and those watching their weight. Monk fruit is often used in a variety of food and drink products and can be a great substitute for sugar in recipes.
Sweetener | Source | Glycemic Index | Nutritional Benefits | Common Uses |
Honey | Bee-produced nectar | Medium | Antioxidants, antibacterial properties | Tea, baking, sauces |
Maple Syrup | Maple tree sap | Low | Manganese, zinc, calcium | Pancakes, oatmeal, desserts |
Stevia | Stevia plant | 0 | Zero-calorie, suitable for diabetics | Sweetener for drinks, baking |
Monk Fruit | Monk fruit | 0 | Zero-calorie, high in antioxidants | Beverages, low-calorie foods |
Coconut Sugar | Coconut sap | Low | Iron, calcium, potassium | Baking, sweetening dishes |
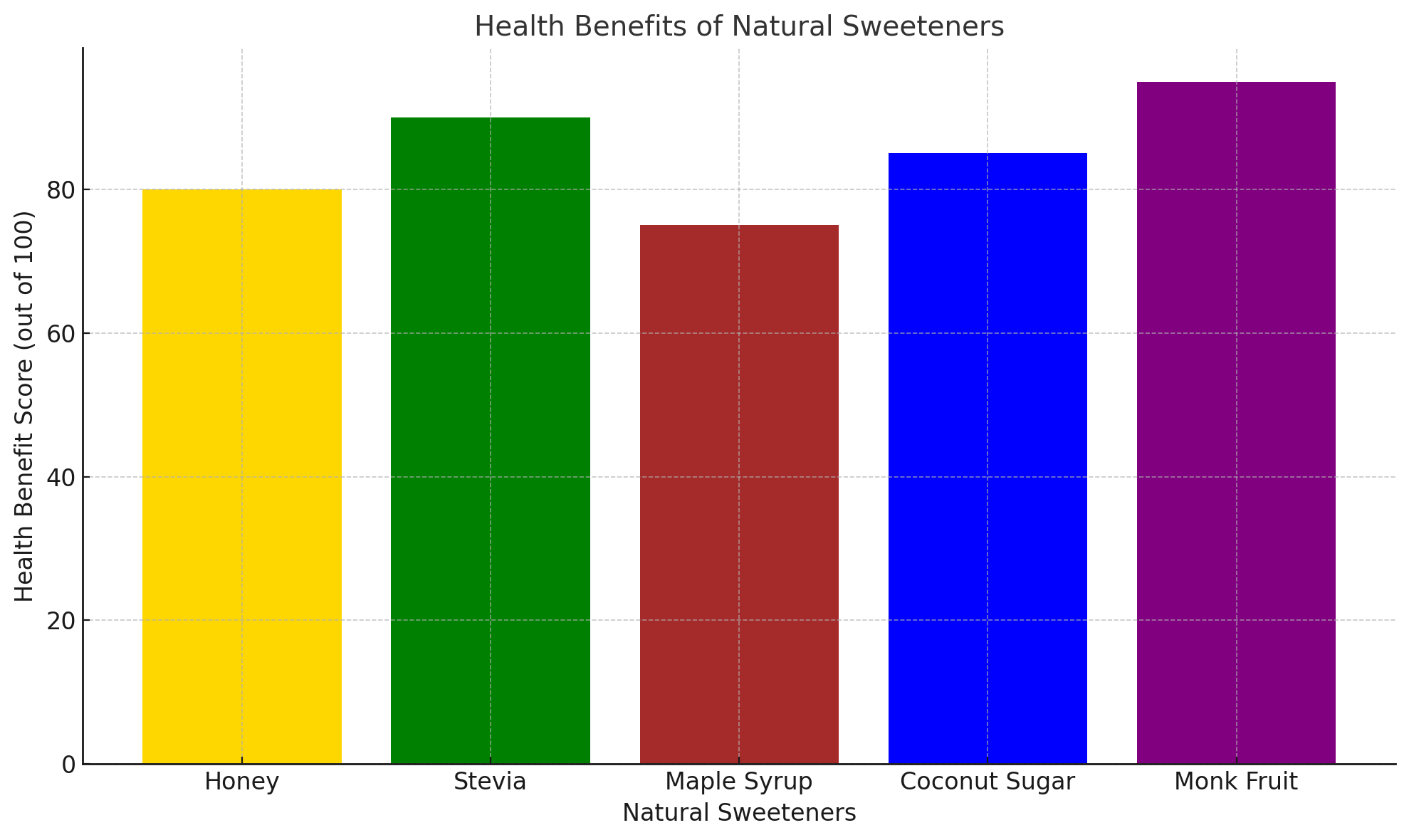
Pros and Cons of Natural Sweeteners
Pros
Natural sweeteners offer a range of benefits, including their nutritional value, lower glycemic index, and more natural processing compared to refined sugars. Many natural sweeteners contain antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, which can support health and provide additional benefits beyond sweetness. Additionally, natural sweeteners are often less processed, making them a more eco-friendly and sustainable option.
Cons
Despite their benefits, natural sweeteners still contain sugar and calories, so moderation is essential. For example, honey and maple syrup can raise blood sugar levels, which may not be suitable for people with diabetes. Some natural sweeteners, such as agave syrup, can still contribute to excessive calorie intake if consumed in large quantities.
Sweetener | Health Benefits | Best For |
Honey | Rich in antioxidants, anti-inflammatory properties | Immune support, energy boost |
Stevia | Zero-calorie, helps manage blood sugar | Diabetics, weight management |
Maple Syrup | Contains minerals like manganese and zinc | Bone health, antioxidants |
Monk Fruit | Zero-calorie, reduces inflammation | Weight loss, blood sugar control |
Date Sugar | High in fiber, minerals like potassium | Digestive health, energy |
Natural Sweeteners vs. Artificial Sweeteners
Taste and Flavor Profiles
Natural sweeteners offer a wider range of flavors than artificial sweeteners, which often have a metallic aftertaste. Honey, for instance, adds floral, earthy notes, while maple syrup offers a caramel-like flavor. Stevia and monk fruit, on the other hand, provide sweetness without the calories. Each natural sweetener brings its unique taste, making it easier for consumers to find one that fits their preferences.
Health Benefits and Risks
Natural sweeteners tend to offer health benefits that artificial sweeteners cannot match. Many contain antioxidants and essential nutrients that support overall health. In contrast, artificial sweeteners typically offer no nutritional value and may have side effects, such as headaches or digestive issues, in some individuals. Choosing natural sweeteners provides an opportunity to enjoy sweetness while supporting your health.
Use in Cooking and Baking
Natural sweeteners are versatile and can be used in a wide variety of recipes. Some, like honey and maple syrup, can be used as one-to-one replacements for sugar in cooking and baking, while others, like stevia and monk fruit, require adjustments to the recipe. It's important to understand the specific characteristics of each sweetener and make the necessary changes to ensure successful results in your dishes.
How to Choose the Right Natural Sweetener
Consider Health Goals
When selecting a natural sweetener, it's important to consider your health goals. For people with diabetes, sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit are ideal because they don't affect blood sugar. If you're aiming to increase your intake of antioxidants and minerals, honey and maple syrup may be better options.
Taste Preferences
Different natural sweeteners bring distinct flavor profiles. Honey has a floral sweetness, maple syrup offers a rich, caramel-like flavor, and stevia provides a clean, sweet taste without the calories. The best natural sweetener for you will depend on your taste preferences and the dishes you plan to prepare.
Considerations for Cooking and Baking
Not all natural sweeteners behave the same way in recipes. Some, like honey and maple syrup, add moisture and can replace sugar in liquid-based recipes. Others, like stevia and monk fruit, are highly concentrated and should be used in smaller quantities. Adjusting your recipes accordingly will help ensure you get the best results.
Sweetener | Equivalent to 1 Cup of Sugar | Notes on Usage |
Honey | 3/4 cup | Reduces liquid in recipe by 3-4 tbsp |
Maple Syrup | 3/4 cup | Adds a caramel-like flavor |
Stevia | 1 tsp (concentrated form) | Requires adjustments for texture |
Coconut Sugar | 1 cup | Similar texture to brown sugar |
Monk Fruit | 1/2 cup | Less sweet than sugar, needs adjustment |
Future of Natural Sweeteners
Popularity Growth
As people become more health-conscious, the demand for natural sweeteners continues to rise. Consumers are increasingly seeking healthier alternatives to refined sugar, and natural sweeteners provide a way to satisfy sweet cravings without the negative health effects associated with sugar.
Innovation in Sweetener Products
New natural sweeteners are being developed, offering even more options for those looking to reduce their sugar intake. As innovation continues, we can expect even more low-calorie and zero-calorie sweeteners to emerge, further enhancing the variety available to consumers.
Conclusion
Natural sweeteners offer a healthier, more nutritious alternative to refined sugar. They provide a variety of flavors and health benefits, such as antioxidants and essential minerals. These sweeteners can be used in different culinary applications, allowing you to reduce sugar intake while still enjoying sweetness. At Zhuhai Huichun Trade Co., Ltd., we offer high-quality natural sweeteners that support a healthier lifestyle and culinary creativity.
FAQ
Q: What are natural sweeteners?
A: Natural sweeteners are derived from plants or animals with minimal processing, offering a healthier alternative to refined sugar.
Q: How do natural sweeteners affect blood sugar levels?
A: Many natural sweeteners, like stevia and monk fruit, have little to no impact on blood sugar, making them ideal for those managing diabetes.
Q: Are natural sweeteners healthier than refined sugar?
A: Yes, natural sweeteners often contain beneficial compounds such as antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making them a healthier option than refined sugar.
Q: Can I use natural sweeteners in cooking?
A: Absolutely! Natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and stevia can be used in a variety of recipes, though adjustments may be needed for sweetness and texture.
Q: Why should I choose natural sweeteners over artificial sweeteners?
A: Natural sweeteners offer a more nutritious, less processed option and provide health benefits, unlike artificial sweeteners which may lack nutrients.















