Introduction
Managing sugar intake is a crucial challenge for diabetics. Traditional sugar can cause harmful blood sugar spikes, making it vital to find alternatives. Enter natural sweeteners—offering a safe solution without the same risks. But what is the best natural sweetener for diabetics?
In this article, we’ll examine popular natural sweeteners, their impact on blood sugar, and their benefits. You’ll learn which options are healthiest and most effective for managing diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes and Sugar’s Impact
The Role of Sugar in Blood Glucose Levels
For diabetics, controlling blood glucose levels is crucial. Consuming foods high in sugar leads to rapid spikes in blood sugar, which can cause a variety of health issues over time. These include long-term complications such as nerve damage, heart disease, and kidney problems. Refined sugars, such as sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup, are particularly concerning due to their quick digestion and significant effect on insulin production.
Since the body of a diabetic is less effective at managing blood glucose levels, it’s vital to find alternatives that won’t cause dramatic fluctuations. Natural sweeteners provide a way to enjoy sweetness without the same impact as regular sugar, but choosing the right one is essential.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Sweetener
It’s essential for diabetics to select sweeteners that have a minimal effect on blood glucose. Some sweeteners, while labeled as “natural,” still contain high levels of fructose or glucose that can elevate blood sugar. By choosing the right natural sweeteners, you can satisfy your sweet cravings without compromising your health.
Key Criteria for Choosing a Sweetener for Diabetics
When selecting a sweetener for diabetics, there are several key factors to consider. These include the glycemic index (GI), the calorie and carbohydrate content, and the long-term safety of the sweetener.
Glycemic Index (GI)
The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood glucose levels. For diabetics, foods with a low GI are preferable, as they result in a slower, more stable increase in blood sugar. Natural sweeteners with a low GI can help manage blood sugar without triggering a spike. For example, stevia and monk fruit are both natural sweeteners with a GI of 0, meaning they won’t raise blood sugar levels.
Choosing sweeteners with a low GI is crucial for blood sugar management and helps reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
Calories and Carbohydrates
For many diabetics, controlling calorie and carbohydrate intake is just as important as managing blood sugar. While some natural sweeteners are calorie-free and carb-free (like stevia and monk fruit), others, like coconut sugar and honey, still contain significant amounts of carbohydrates and calories.
It’s essential to balance your sweetener choice with your dietary needs. Opting for a sweetener with minimal calories and carbohydrates will help you keep your blood sugar levels in check while still allowing you to enjoy a sweet treat.
Safety and Long-Term Effects
While natural sweeteners are generally considered safer than refined sugars, long-term safety should still be a consideration. Some natural sweeteners, like stevia, have been extensively studied and found to be safe for daily use. However, others, like erythritol, should be consumed in moderation, as excessive use can lead to digestive discomfort. It’s always best to stay informed about potential side effects and choose sweeteners backed by scientific research.
Sweetener | Calories | Glycemic Index (GI) | Effect on Blood Sugar |
Regular Sugar | 16 kcal/tsp | 65-70 | Significant Spike |
Stevia | 0 | 0 | None |
Monk Fruit | 0 | 0 | None |
Erythritol | 0.24 kcal/g | 0 | Minimal |
Allulose | ~0.2 kcal/g | Close to 0 | Minimal |
Best Natural Sweeteners for Diabetics
Here’s a closer look at some of the best natural sweeteners that are ideal for people with diabetes.
Stevia
Stevia is a highly popular natural sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant. It’s calorie-free, carb-free, and has a glycemic index of 0, making it an excellent choice for diabetics. Stevia can help control blood sugar levels without adding extra calories or carbohydrates to your diet.
While stevia is generally safe, some people report a bitter aftertaste, especially in higher concentrations. It’s best to start with a small amount and see how you like the taste.
Monk Fruit
Monk fruit, also known as Luo Han Guo, is another natural sweetener with zero calories and zero carbohydrates. It’s made from the extract of monk fruit, which contains mogrosides—antioxidants that provide sweetness without affecting blood sugar levels.
Monk fruit is a great option for diabetics looking for a sweetener with antioxidant benefits. However, it can be more expensive than other sweeteners, and some monk fruit products may contain added fillers. Always check the label to ensure you’re getting pure monk fruit extract.
Erythritol
Erythritol is a sugar alcohol found naturally in fruits like melons and grapes. It’s virtually calorie-free and has a glycemic index of 0, making it an excellent choice for diabetics. Erythritol doesn’t raise blood sugar or insulin levels, and it behaves similarly to sugar in terms of texture and sweetness.
However, some people may experience digestive issues, such as bloating or gas, when consuming sugar alcohols like erythritol. It’s best to start with small amounts to see how your body reacts.
Allulose
Allulose is a “rare sugar” that is found naturally in small amounts in fruits like figs and raisins. It has a glycemic index close to 0 and contains very few calories. Allulose tastes like sugar but doesn’t cause a blood sugar spike, making it a great option for diabetics.
Though allulose is safe for most people, it may cause digestive discomfort in large quantities. Like erythritol, it’s best to consume allulose in moderation.
Sweetener | Calories | Glycemic Index (GI) | Impact on Blood Sugar | Best Use |
Stevia | 0 | 0 | None | Baking, drinks, desserts |
Monk Fruit | 0 | 0 | None | Baking, drinks |
Erythritol | 0.24 kcal/g | 0 | Minimal | Baking, sweetening drinks |
Allulose | ~0.2 kcal/g | Close to 0 | Minimal | Baking, desserts, drinks |
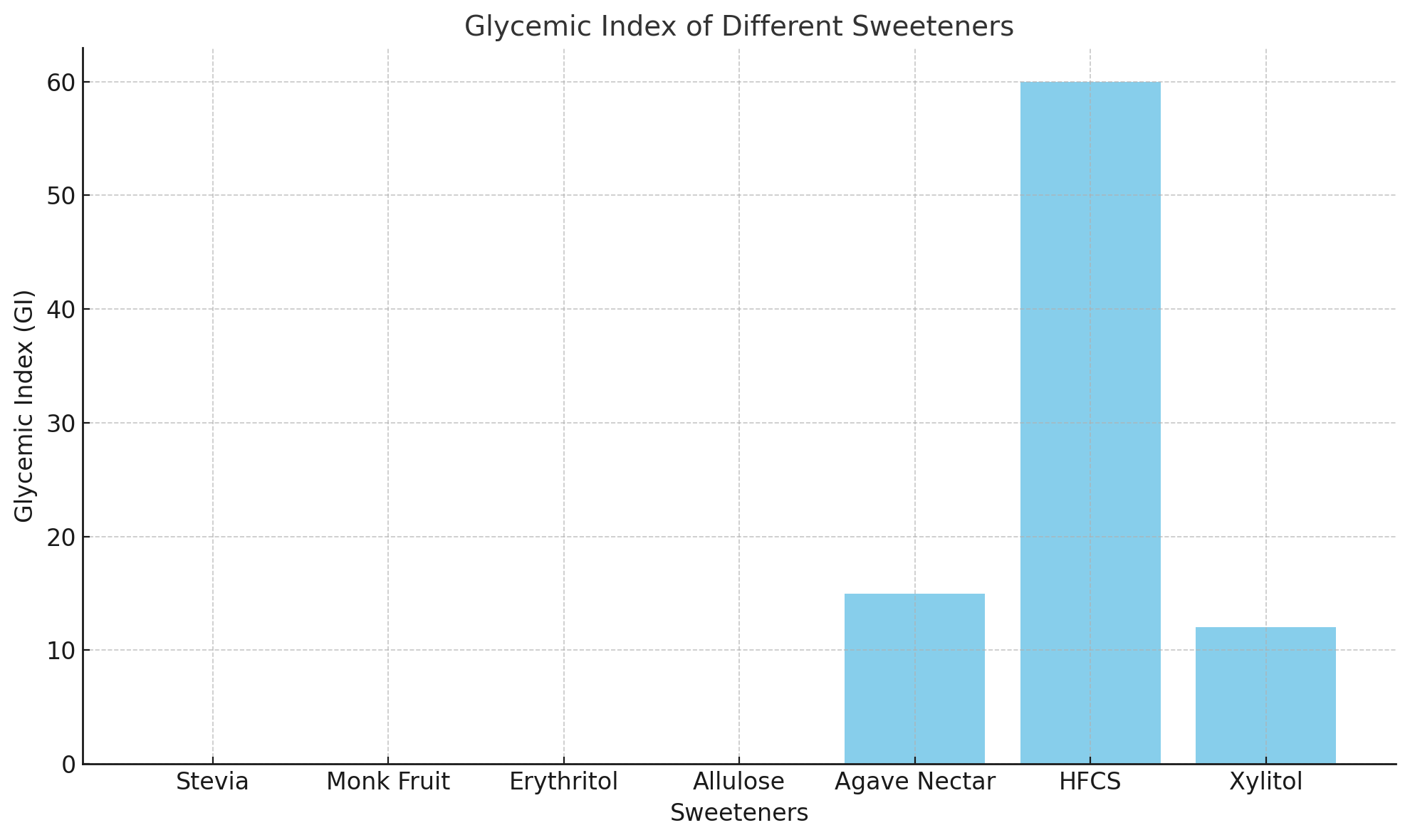
Sweeteners to Avoid for Diabetics
While many natural sweeteners can offer a safe alternative to sugar, some should be avoided by diabetics due to their high glycemic index or potential negative health effects.
Agave Nectar
Agave nectar is often marketed as a healthier substitute for sugar due to its low glycemic index. However, it contains a high level of fructose, which can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels over time. Fructose can also contribute to insulin resistance, making it a poor choice for diabetics. Even though it may seem like a better option, it is best to avoid agave nectar to prevent unwanted blood sugar spikes.
High-Fructose Corn Syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) is a highly processed sweetener commonly found in many processed foods, including sodas, snacks, and even sauces. Despite its affordability and widespread use, HFCS is known to have a high glycemic index. This means it can lead to rapid and significant spikes in blood glucose levels, which can be especially harmful for diabetics. HFCS should be strictly avoided to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Xylitol and Other Sugar Alcohols
Sugar alcohols like xylitol are often used as lower-calorie alternatives to sugar, and while they do not raise blood sugar levels as dramatically, they can still have an effect on insulin. Additionally, sugar alcohols may cause digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea, particularly when consumed in large amounts. Diabetics should be cautious with sugar alcohols, using them sparingly and closely monitoring their body’s response to avoid unwanted side effects.
Sweetener | Reason to Avoid |
Agave Nectar | High fructose content, can increase insulin resistance |
High-Fructose Corn Syrup | Raises blood sugar and increases insulin resistance |
Xylitol | Can cause digestive discomfort (bloating, gas, diarrhea) |
Practical Tips for Incorporating Natural Sweeteners
Choosing the Right Sweetener for Different Recipes
When using natural sweeteners in cooking or baking, it's important to choose the right one based on the type of recipe. For beverages and desserts, stevia and monk fruit are great choices as they dissolve easily and don't affect the texture of drinks or sweets. These sweeteners offer sweetness without adding calories or raising blood sugar levels. On the other hand, erythritol and allulose are perfect for baking. They have a texture and sweetness level closer to sugar, making them ideal for recipes that require browning or a more traditional sugar-like texture. Always consider how the sweetener behaves in different cooking or baking environments to get the best results.
Moderation and Balance in the Diet
While natural sweeteners are a healthier alternative to refined sugar, they should still be used in moderation. Overconsumption of any sweetener, even natural ones, can impact your blood sugar and overall health. It's important to balance your intake of sweeteners with a nutrient-dense diet rich in whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins. By focusing on a well-rounded diet and using sweeteners sparingly, you can maintain healthy blood sugar levels while still enjoying the occasional sweet treat. Remember to monitor your blood sugar regularly to ensure your dietary choices are supporting your overall health goals.
Sweetener | Best Use | Common Products |
Stevia | Beverages, baking, desserts | Teas, coffee, cakes, cookies |
Monk Fruit | Beverages, baking | Drinks, desserts, smoothies |
Erythritol | Baking, sweetening drinks | Cookies, cakes, sugar substitutes for drinks |
Allulose | Baking, desserts, sweetening drinks | Cookies, candies, yogurt |
Expert Opinions on Natural Sweeteners and Diabetes Management
Nutritionist and Doctor Insights
Many health professionals recommend natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit for diabetics due to their minimal impact on blood glucose. Nutritionists suggest that these sweeteners can be part of a healthy diet, but they should be used in moderation alongside other diabetes management strategies, such as exercise and medication.
Scientific Research on Long-Term Use of Natural Sweeteners
Ongoing studies continue to explore the long-term effects of natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit on blood sugar control and overall health. Current evidence suggests these sweeteners are safe and effective for managing diabetes, but more research is needed to fully understand their long-term effects.

Conclusion
Choosing the right natural sweetener is essential for diabetics to manage blood glucose levels. Stevia, monk fruit, erythritol, and allulose offer healthy alternatives to sugar with minimal blood sugar impact. Moderation is key, and maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health. For those seeking high-quality natural sweeteners, Zhuhai Huichun Trade Co., Ltd. provides reliable options that cater to diabetic-friendly diets, ensuring a sweet yet healthy solution.
FAQ
Q: What are natural sweeteners for diabetics?
A: Natural sweeteners like stevia, monk fruit, and erythritol are great alternatives to sugar. They have little to no impact on blood sugar, making them suitable for diabetics.
Q: Why should diabetics choose natural sweeteners?
A: Diabetics should choose natural sweeteners because they are low in glycemic index, helping control blood sugar levels without causing spikes, unlike regular sugar.
Q: Can natural sweeteners still affect blood sugar?
A: While most natural sweeteners have minimal effects on blood sugar, it's important to consume them in moderation. Some may still impact glucose levels if consumed excessively.
Q: Which natural sweetener is best for baking?
A: Stevia and erythritol are popular natural sweeteners for baking due to their heat stability and low glycemic impact, making them ideal choices for diabetics.
Q: Are natural sweeteners calorie-free?
A: Many natural sweeteners, like stevia and monk fruit, are calorie-free. However, others like erythritol and allulose contain small amounts of calories but are still very low compared to sugar.















